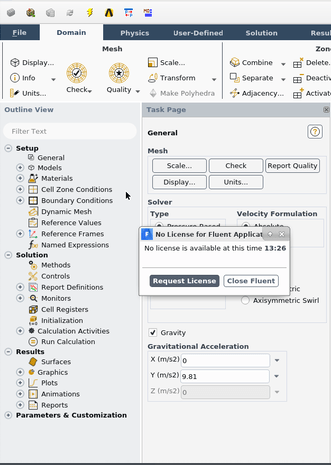
The usage of Fluent was smooth. But when I launched the Fluent (Fluent with Meshing)
I’ve got this error. “No license is available at this time”
Taking a look at ANSYS Learning Forum, According to the forum (Licensing error while opening ANSYS Mechanical) “That error message would appear when there is another operation going on that won’t allow the license to be shared , such as meshing or solving, etc.”
To resolve the issue:
- Execute the command “/usr/local/ansys_inc/v195/commonfiles/tools/linx64/ansyslm_relutil -userprefs
You should see the dialog box.
You have to go to the bottom of the dialog box “When using Workbench, would you like to”, Use a separate license for each application
Finally, close the application and restart. The issue should go away.
References: