If you are using Active Directory, you may only have uid for ownership to locate the directory, the command to use will be
cd /home
find . -maxdepth 1 -user 130456785323
lostuserIf you are using Active Directory, you may only have uid for ownership to locate the directory, the command to use will be
cd /home
find . -maxdepth 1 -user 130456785323
lostuserIf you are writing a script that involve cat and if you wish to leave a line after “cat”, do the following
cat /usr/local/lic_lmstat_log/abaqus_lmstat.log ; echo.....
.....
Users of tfluid_int_ccmp: (Total of 128 licenses issued; Total of 0 licenses in use)
Users of tfluid_int_fluent: (Total of 128 licenses issued; Total of 0 licenses in use)
[user1@node1 ~]$
If you need to change the timestamp recursively, you may want to use the command. Change to the directory where you want to change.
$ cd ToBeChangedDir
$ find * -exec touch -t 202403011000 {} \;Finally change the root directory itself
$ touch -t 202403011000 ToBeChangedDirI had a casual read on the book “Bash Idioms” by Carl Albing. I scribbled what I learned from what stuck me the most. There are so much more. Please read the book instead.
Lesson 1: “A And B” are true only if both A and B are true…..
Example 1: If the cd command succeeds, then execute the “rm -Rv *.tmp” command
cd tmp && rm -Rv *.tmpLesson 2: If “A is true”, “B is not executed” and vice versa.
Example 2: Change Directory, if fail, put out the message that the change directory failed and exit
cd /tmp || { echo "cd to /tmp failed" ; exit ; }Lesson 3: When do we use the [ ] versus [[ ]]?
I learned that the author advises BASH users to use the [[ ]] unless when avoidable. The Double Bracket helps to avoid confusing edge case behaviours that a single bracket may exhibit. If however, the main goal is portability across various platform to non-bash platforms, single quota may be advisable.
You may use the command “telinit” to change the SysV system runlevel without the need to reboot. You will need root access to run the command
Use 1: Single User Mode
# telinit SUse 2: To go to Graphical.Target
# telinit 5Use 3: To go to Multi-User.Target
# telinit 3Use 4: To Reload daemon configuration. This is equivalent to systemctl daemon-reload.
# telinit qTo verify, you can use the command systemctl get-default
# systemctl get-default
graphical.targetAlias are very useful tools to create shorthand pseudonyms to run the command you want without typing the whole thing.
Display all alias names
Typing alias the whole command will
$ alias
alias cp='cp -i'
alias egrep='egrep --color=auto'
alias fgrep='fgrep --color=auto'
alias grep='grep --color=auto'
alias l.='ls -d .* --color=auto'
alias ll='ls -l --color=auto'
alias ls='ls --color=auto'
alias mv='mv -i'
alias rm='rm -i'
alias xzegrep='xzegrep --color=auto'
alias xzfgrep='xzfgrep --color=auto'
alias xzgrep='xzgrep --color=auto'
alias zegrep='zegrep --color=auto'
alias zfgrep='zfgrep --color=auto'
alias zgrep='zgrep --color=auto'
Useful Alias to consider
alias ls='ls --color=auto'
alias egrep='egrep --color=auto'
alias fgrep='fgrep --color=auto'
alias grep='grep --color=auto'
alias mv='mv -i'
alias rm='rm -i'
alias cp='cp -i'Remove alias
Just use the command unalias
unalias ll I was having an issue with my expect script
spawn ssh licensecheck@192.168.1.0
Password:
Authentication failed.
send: spawn id exp6 not open
while executing
.....
.....
This my code…..
#!/usr/bin/expect
set timeout 20
spawn ssh -o PubkeyAuthentication=no licensecheck@192.168.1.0
expect "Password: " {send "mypassword\r"}
expect "$ " {send "/usr/xxx/xxx/xxx/lmstat -a\r"}
expect "$ " {send "exit\r"}
Do check out whether the expression is correct. In case, I leave a space after “Password: ” After I remove, the space, the error is gone. There is also a write-up in a form. Do take a look at Linux – spawn_id: spawn id exp6 not open
Point 1: View all the saved connections
# nmcli connection show
ens1f0 XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX ethernet ens1f0
ens1f1 YYYY-YYYY-YYYY-YYYY-YYYY ethernet ens1f1
ens10f0 ZZZZ-ZZZZ-ZZZZ-ZZZZ-ZZZZ ethernet --
ens10f1 AAAA-AAAA-AAAA-AAAA-AAAA ethernet --
Point 2a: Stop Network
You can use the command “nmcli connection down ssid/uuid". For example
# nmcli connection down XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX
Connection 'eno0' successfully deactivated (D-Bus active path: /org/freedesktop/NetworkManager/ActiveConnection/3)Point 2b: Start Network
You can use the command “nmcli connection up ssid/uuid". For example
# nmcli connection up XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX
Connection 'eno0' successfully activated (D-Bus active path: /org/freedesktop/NetworkManager/ActiveConnection/3)Point 3: Device Connection
To check the Device status
# nmcli dev status
ens1f0 ethernet connected ens1f0
eno1f1 ethernet connected ens1f1
eno10f0 ethernet disconnected --
eno10f1 ethernet disconnected --
Point 4: List all Device
# nmcli device show
GENERAL.DEVICE: ens1f0
GENERAL.TYPE: ethernet
GENERAL.HWADDR: XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
GENERAL.MTU: 1500
GENERAL.STATE: 100 (connected)
GENERAL.CONNECTION: ens1f0
GENERAL.CON-PATH: /org/freedesktop/NetworkManager/ActiveConnection/2
WIRED-PROPERTIES.CARRIER: on
IP4.ADDRESS[1]: 192.168.0.1
IP4.GATEWAY: 192.168.0.254
IP4.ROUTE[1]: dst = 0.0.0.0/0, nh = 192.168.0.254, mt = 101
IP4.ROUTE[2]: dst = 198.168.0.0/19, nh = 0.0.0.0, mt = 101
IP6.ADDRESS[1]: xxxx::xxxx:xxxx:xxxx:xxxx/64
IP6.GATEWAY: --
IP6.ROUTE[1]: dst = fe80::/64, nh = ::, mt = 1024
GENERAL.DEVICE: eno1f1
GENERAL.TYPE: ethernet
GENERAL.HWADDR: 94:6D:AE:9B:76:1C
GENERAL.MTU: 1500
GENERAL.STATE: 100 (connected)
GENERAL.CONNECTION: eno1f1
GENERAL.CON-PATH: /org/freedesktop/NetworkManager/ActiveConnection/4
WIRED-PROPERTIES.CARRIER: on
IP4.ADDRESS[1]: 192.168.200.201/19
IP4.GATEWAY: --
IP4.ROUTE[1]: dst = 192.168.192.0/19, nh = 0.0.0.0, mt = 102
IP6.ADDRESS[1]: fe80::966d:aeff:fe9b:761c/64
IP6.GATEWAY: --
IP6.ROUTE[1]: dst = fe80::/64, nh = ::, mt = 1024
Point 5: Start and Stop Device
# nmcli con down ens1d1
# nmcli con up ens1d1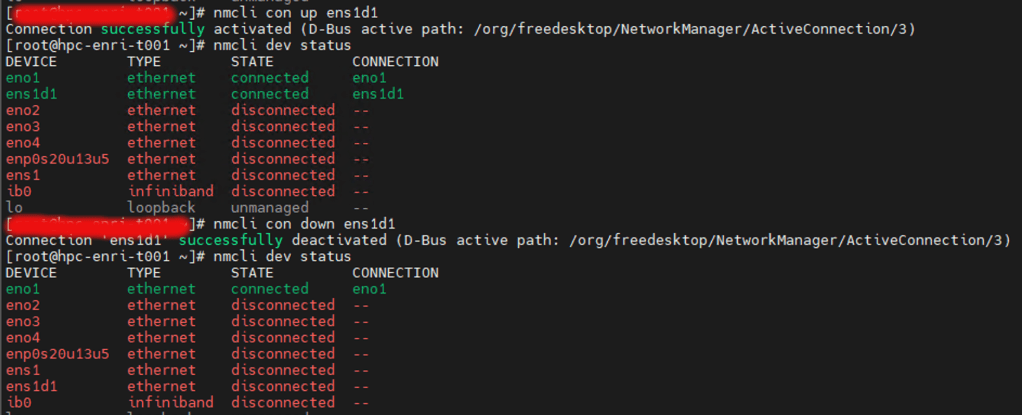
References:
Listing files by access date.
You can use the “-ltur” option. The “u” enforces the “by access date” listing order. The “t” option to list files in order of age. The “r” option is to reverse the option
$ ls -ltur
-rwxr-xr-x 1 user1 users 1622374400 Mar 10 00:08 yyyy.iso
-rw-rw-r-- 1 user1 users 18387452 Mar 13 14:06 xxxx.rpm
-rwxr-xr-x 1 user1 users 303 Mar 30 16:32 visJob.pbs
-rw------- 1 user1 users 762 Mar 30 16:35 visJob.o1475403
-rw------- 1 user1 users 59 Mar 30 16:35 visJob.e1475403
Listing Files by Modified Date and Time
You can use the “-ltr” option. The “r” is the reverse order.
$ ls -ltr
-rw-rw-r-- 1 melvin melvin 18387452 Mar 13 14:03 xxxx.rpm
-rwxr-xr-x 1 melvin melvin 303 Mar 13 17:00 vis.pbs
-rw-rw-r-- 1 melvin melvin 1084 Mar 23 16:52 yyy.pem
Listing files by owner
Use the output of the ls command to sort and pick out the owner column by adding “-k3” to sort on the third field.
$ ls -l | sort -k3 | more
drwx------ 29 www users 1005 Sep 20 2022 www-home
drwx------ 16 yyy users 684 Apr 3 14:07 yyy-home
drwx------ 16 zzz users 746 Mar 21 11:31 zzz-home
Listing files by group
Sort files by the associated groups, you can pass the output from a long listing to the sort command and tell it to sort on column 4.
$ ls -l | sort -k4 | more
drwx------ 29 www users1 1005 Sep 20 2022 www-home
drwx------ 16 yyy users2 684 Apr 3 14:07 yyy-home
drwx------ 16 zzz users3 746 Mar 21 11:31 zzz-home
Listing files by size
To sort files by Size, use the “-S” Option. If you wish to put the largest files at the end, use the “-r”. Use the “-h” to be human readable.
ls -lSrh
-rw-rw-r-- 1 www users 1.9G Nov 15 11:04 integr8_120.xml.gz
-rw-rw-r-- 1 www users 6.0G Jul 26 2022 20220712_msconvert.zip
-rw-rw-r-- 1 www users 6.9G May 31 2022 ELECTRONICS.tgz
Basic Use of FIND
If you are looking to find a file, one of the most common tools is Find. Here is a recap.
| O | FILE TYPE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | type -f | Limits search results to files only |
| 2 | type -d | Limits search results to directories only |
| 3 | type -l | Limits search results to symbolic links only |
For example, search for a case-insensitive file named “hello.mov”
$ find $HOME -type -iname "Hello.mov"Parameters
| NO | PARAMETERS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | -name | Perform a case-sensitive search for “files” |
| 2 | -iname | Perform a case-insensitive search for “files” |
| 3 | size +n | Matches files of size larger than size n |
| 4 | size -n | Matches files of size smaller than size n |
| 5 | -mtime n | Matches files or directories whose contents were last modified n*24 hours ago |
| 6 | -atime n | Matches files last access n*24 hours ago |
For example, search for all case-insensitive files with the extension *mov 2 days ago
$ find $HOME -type -iname "*.mov" -mtime 2Operators
| S/NO | OPERATOR | EXPLANATION |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | -and | Match for both sides of the operators |
| 2 | -or | Match for either test of the operators |
| 3 | -note | Don’t match the test of the operators |
For example, search for all files with Hello*, but excl ude pdf and jpg
$ find \( -name "Hello*" -mtime 2 \) -and -not \( -iname "*.jpg" -or -iname "*.pdf" \)When using the () to combine tests, remember to escape the (\) brackets. You will need to leave a space after you open and close the brackets
find -type f -iname "*.mov" -exec chmod +x {} \;The first part find -type f -iname”*.mov” will not be explained….. Executed commands must end with \; (a backslash and semi-colon) and may use {} (curly braces) as a placeholder for each file that the find command locates.
References: