The Working of a Copy-on-Write System In Brief
Copy-On-Write Filesystem does not overwrite the data in place, here is how it is done. Supposedly there is file that will be modified.
- Copy the old data to an allocated location on the disk
- New data is written to the allocated location on the disk.
- Hence the name Copy-and-Write
- The references for the new data are updated
- However, the old data and its snapshots are still there

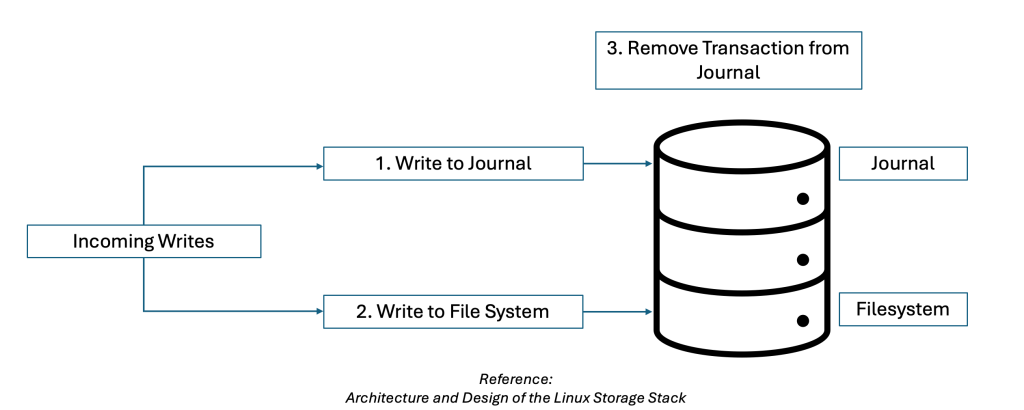
As described in the Architecture and Design of Linux Storage Stack by Muhammad Umer Page 59
As the old data is preserved in the process, filesystem recovery is very simplified. Since the previous state of the data is saved on another allocated location on disk. If there is an outrage, the system system can easily revert to its former state. This make the maintenance of any Journal obsolete. This also allows snapshots to be implemented at the filesystem level.
As the old data is still there, space utilisation may be more than what the user expects……
Some of the filesystem the use the CoW based approach includes Zttabyte Filesystem (ZFS) and B-Tree Filesystem (Btrfs)