Taken from Developing a Linux Kernel Module using GPUDirect RDMA
1.0 Overview
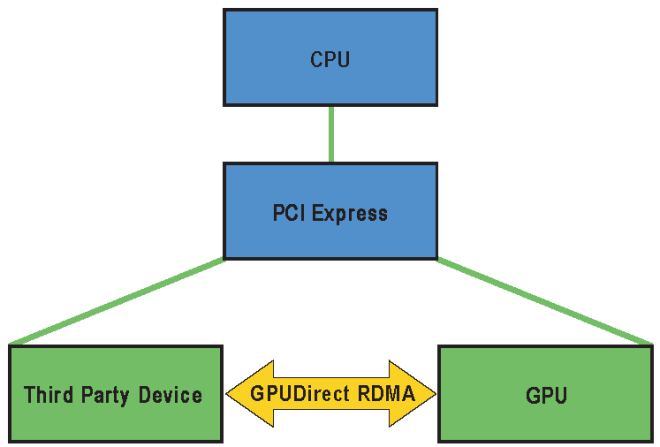
GPUDirect RDMA is a technology introduced in Kepler-class GPUs and CUDA 5.0 that enables a direct path for data exchange between the GPU and a third-party peer device using standard features of PCI Express. Examples of third-party devices are: network interfaces, video acquisition devices, storage adapters.
GPUDirect RDMA is available on both Tesla and Quadro GPUs.
A number of limitations can apply, the most important being that the two devices must share the same upstream PCI Express root complex. Some of the limitations depend on the platform used and could be lifted in current/future products.
A few straightforward changes must be made to device drivers to enable this functionality with a wide range of hardware devices. This document introduces the technology and describes the steps necessary to enable an GPUDirect RDMA connection to NVIDIA GPUs on Linux.
1.1. How GPUDirect RDMA Works
When setting up GPUDirect RDMA communication between two peers, all physical addresses are the same from the PCI Express devices’ point of view. Within this physical address space are linear windows called PCI BARs. Each device has six BAR registers at most, so it can have up to six active 32bit BAR regions. 64bit BARs consume two BAR registers. The PCI Express device issues reads and writes to a peer device’s BAR addresses in the same way that they are issued to system memory.
Traditionally, resources like BAR windows are mapped to user or kernel address space using the CPU’s MMU as memory mapped I/O (MMIO) addresses. However, because current operating systems don’t have sufficient mechanisms for exchanging MMIO regions between drivers, the NVIDIA kernel driver exports functions to perform the necessary address translations and mappings.
To add GPUDirect RDMA support to a device driver, a small amount of address mapping code within the kernel driver must be modified. This code typically resides near existing calls to get_user_pages().
The APIs and control flow involved with GPUDirect RDMA are very similar to those used with standard DMA transfers.
References:
Read more at: http://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/gpudirect-rdma/index.html